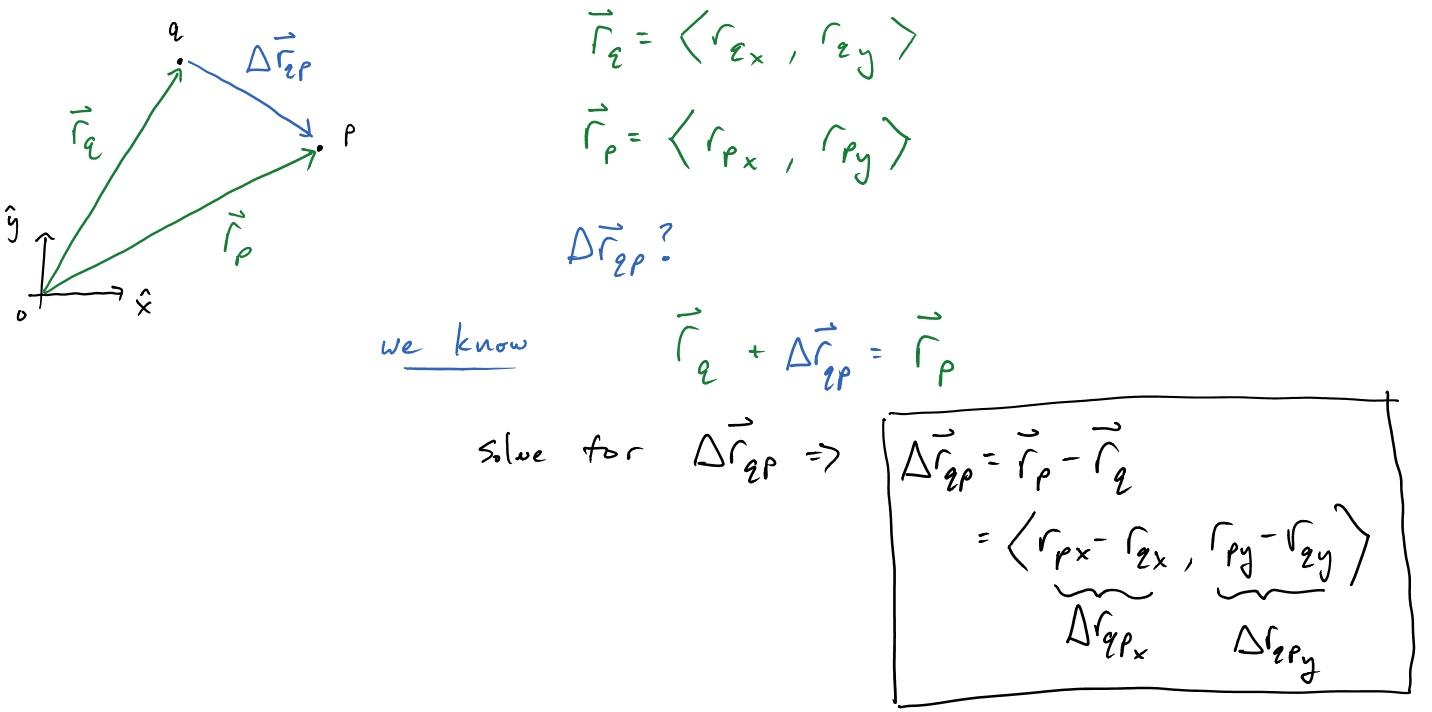Lecture 1 | Position & Displacement
Average Quantities
Lecture 1 | Position & Displacement
Average Quantities
Kinematics is the study of motion through describing and relating the position ($\overrightarrow{r}$), velocity $(\overrightarrow{v})$, and acceleration ($\overrightarrow{a}$) of a system. Average Quantities involves taking snapshots in time of an initial and final state of a system and finding the average of the above quantities. This section is also intended to practice vector mathematics. Operations, like adding or subtracting vectors, is a very important skill in almost all of physics, including kinematics.
One minute motivation: distance vs. displacement!
Pre-lecture Study Resources
Watch the pre-lecture videos and read through the OpenStax text before doing the pre-lecture homework or attending class.
Average Quantities | Position and Displacement
You can define a position vector by it's x and y components.
$\overrightarrow{r}=\langle x, y \rangle$
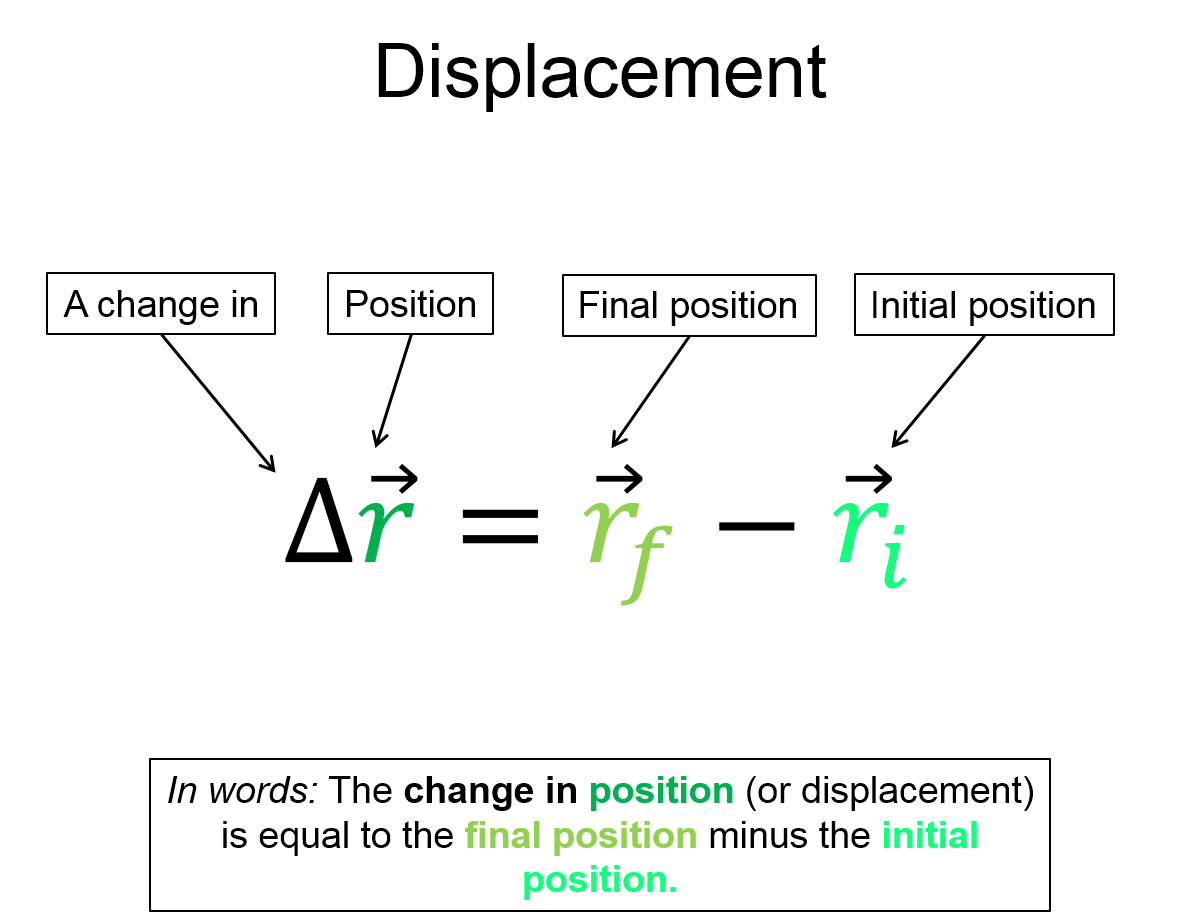
You can also define the change in position (or displacement) as the final position minus the initial position.
$\Delta \overrightarrow{r}=\overrightarrow{r}_f - \overrightarrow{r}_i$
The vector diagram for a situation like this is below. In the case of position vectors, it is also what a birds-eye view might see. The axis, with origin o, defines the point <0, 0> and the positive $\hat{x}$ and positive $\hat{y}$ directions. (Note: the symbol $\hat{x}$ is called x hat and can be thought of as a way to show which direction is the positive x direction. It is technically a unit vector but that formality is unnecessary at this point.) You could imagine an object that begins at point q and after some time, ends at point p. The change in position, labeled $\Delta \overrightarrow{r}_{qp}$ points from the initial position q, to the final position p.
This OpenStax section covers Position and Displacement.