Lecture 2 | Application of 2nd Law: Static Equilibrium & Stability
Statics & Dynamics
Lecture 2 | Application of 2nd Law: Static Equilibrium & Stability
Statics & Dynamics
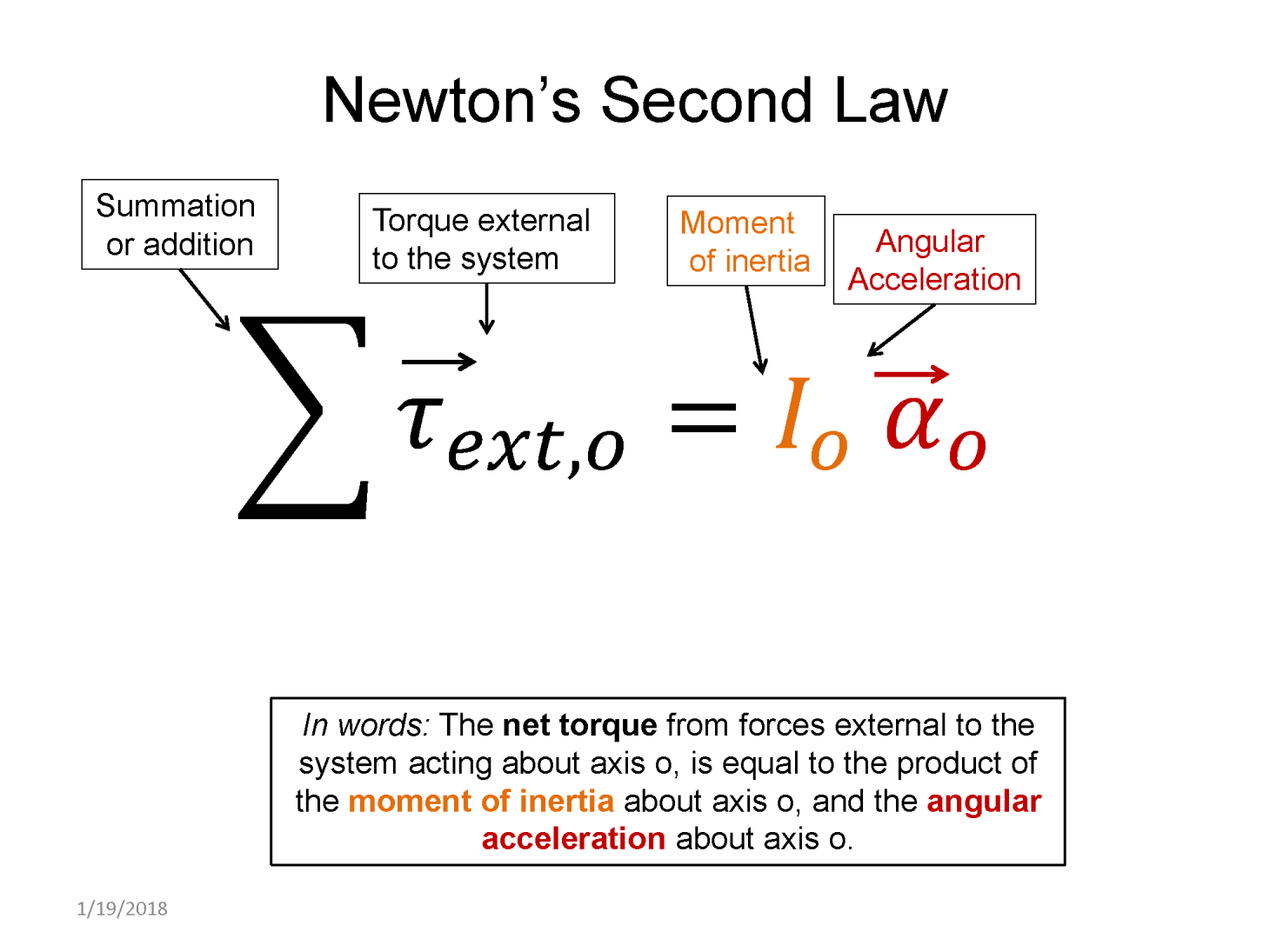
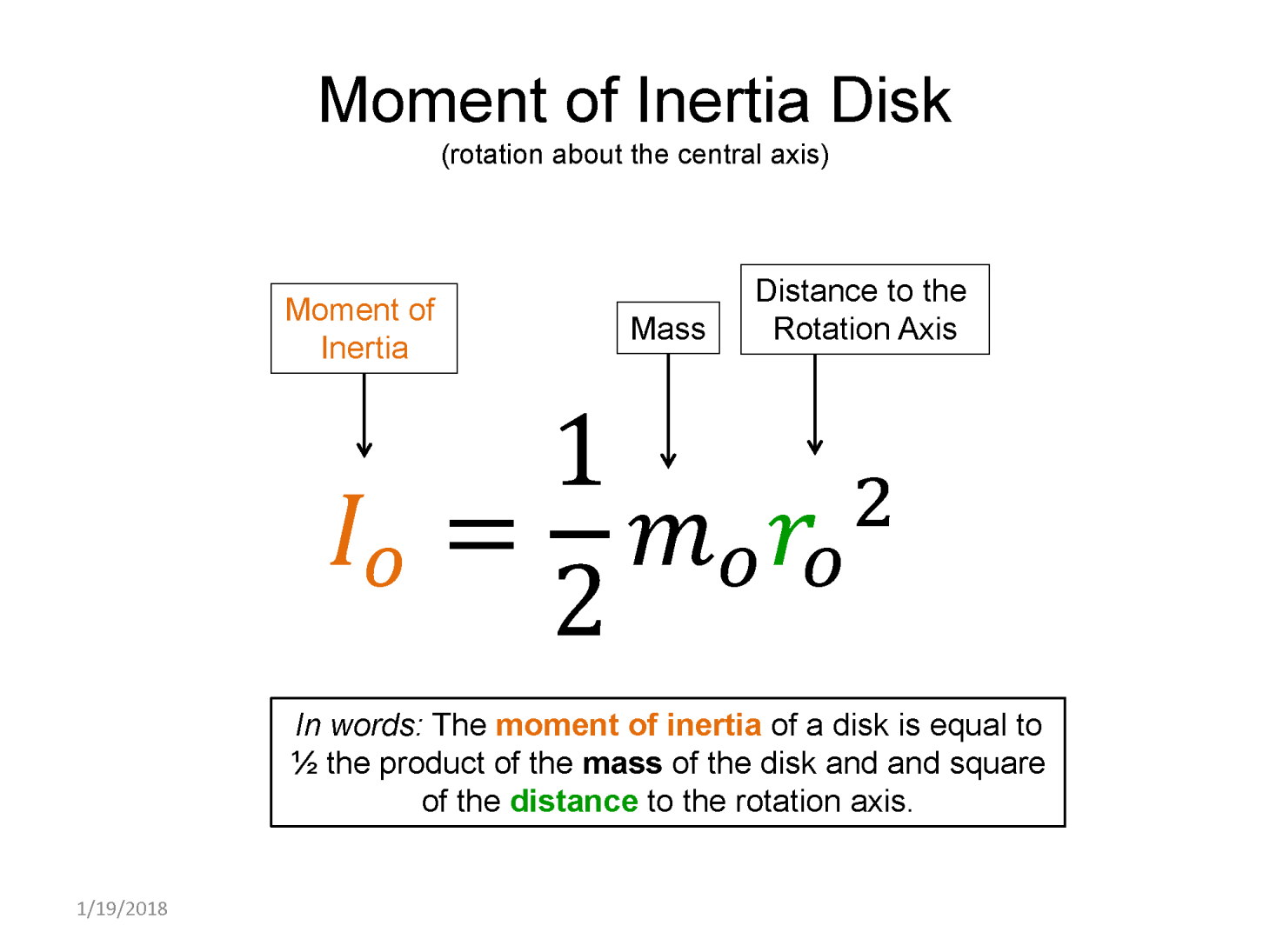
Applying Newton's 2nd law for rotation requires understanding how to calculate torques. Then you add those up and set them equal to the moment of inertia multiplied by the angular acceleration. If an object is in rotational equilibrium, the net torque must add up to zero, resulting in zero angular acceleration.
Check out this short video by OpenStax about both translational and rotational equilibrium.
Pre-lecture Study Resources
Watch the pre-lecture videos and read through the OpenStax text before doing the pre-lecture homework or attending class.
OpenStax Section 9.3 | Stability
OpenStax Section 9.4 | Applications of Statics, Including Problem-Solving Strategies
OpenStax Section 9.5 | Simple Machines
OpenStax Section 9.6 | Forces and Torques in Muscles and Joints