Lecture 1 | Rays, Reflection, Refraction, TIR, Dispersion
Ray Optics
Lecture 1 | Rays, Reflection, Refraction, TIR, Dispersion
Ray Optics
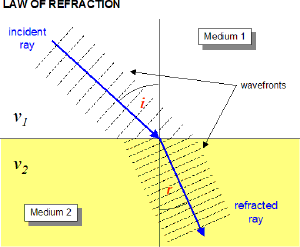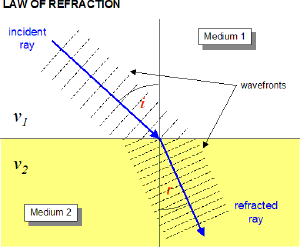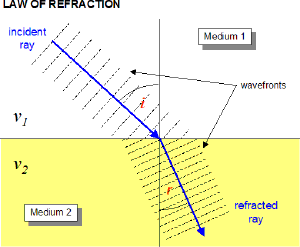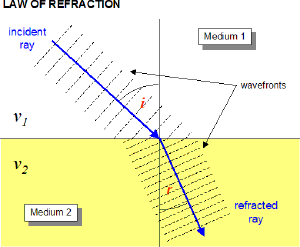
When light travels from one medium into another, direction of motion changes if the index of refraction of the two materials differ. Snell's Law defines how the change of direction relates to the index of refraction of the two materials.
The eye uses refraction to see. Check it out!
Pre-lecture Study Resources
Watch the pre-lecture videos and read through the OpenStax text before doing the pre-lecture homework or attending class.
Ray Optics | Snell's Law of Diffraction
We've learned that light slows down as it enters a material with a higher index of refraction. For continuity of the wave, the frequency must remain constant. If $v=f \lambda$, and the frequency is constant but the speed decreases, the wavelength must also decrease.
OpenStax Section 25.3 | The Law of Refraction
OpenStax Section 25.4 | Total Internal Reflection
OpenStax Section 25.6 | Dispersion: The Rainbow and Prisms