Lecture 3 | Conduction, Convection, Radiation
1st Law & Heat
Lecture 3 | Conduction, Convection, Radiation
1st Law & Heat
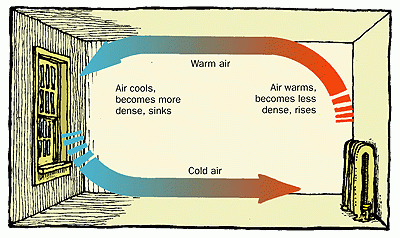
Conduction, convection, and radiation are the three different ways energy can be transfered via heat. Conduction is when energy transfers from one molecule to the next via collisions. Imagine higher energy (greater temp) particles on the inside of a window bumping into their neighbors, when then bump in their neighbors and so on. Eventually some of the thermal energy from the warm side of the window, escapes on the cold side through these collisions. Convection is when a high energy particle literally moves from the a warmer area to a colder area, thus decreasing the thermal energy in the warmer area and increasing it the colder. Radiation is heat transfer electromagnetic waves and all objects with temperature greater than zero (Kelvin) radiate electromagntic waves - think night vision goggles that "see" thermal images.
This concept trailer from OpenStax motivates conduction, convection, and radiation through cooking.
Pre-lecture Study Resources
Watch the pre-lecture videos and read through the OpenStax text before doing the pre-lecture homework or attending class.
Thermo | Heat Transfer Mechanisms: Conduction, Convection, and Radiation
So far we have discussed heat as it relates to the first law of thermodynamics where we learned that heat is a way for systems to exchange energy, similar to work. We then discussed specific heat and heat of transformation under the section "Heat", but really we were just talking about energy transfers where heat was the most common way to transfer that energy, as opposed to work. What have not yet discussed is the specific mechanisms by which energy is transferred via heat. There are three main mechanisms for heat transfer, conduction, convection, and radiation.
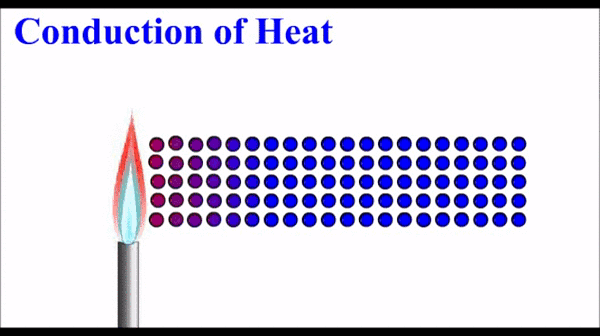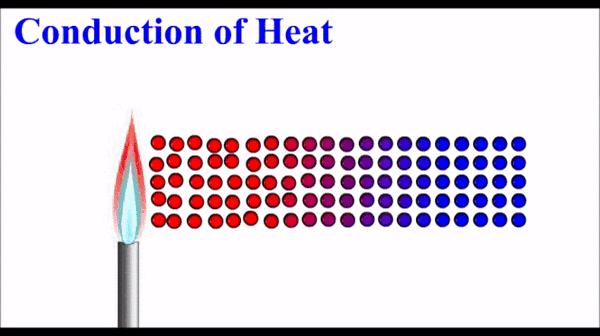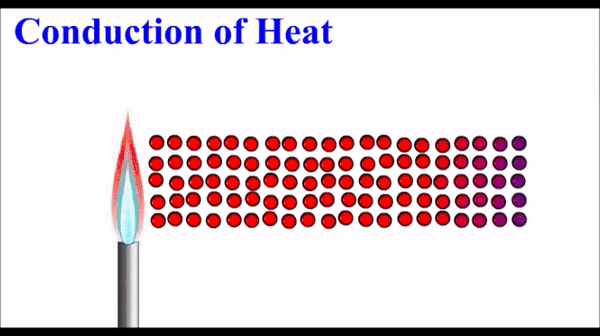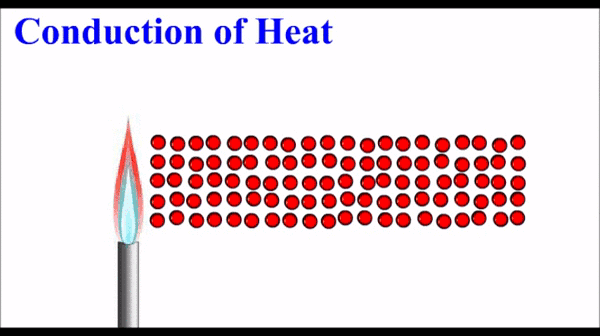
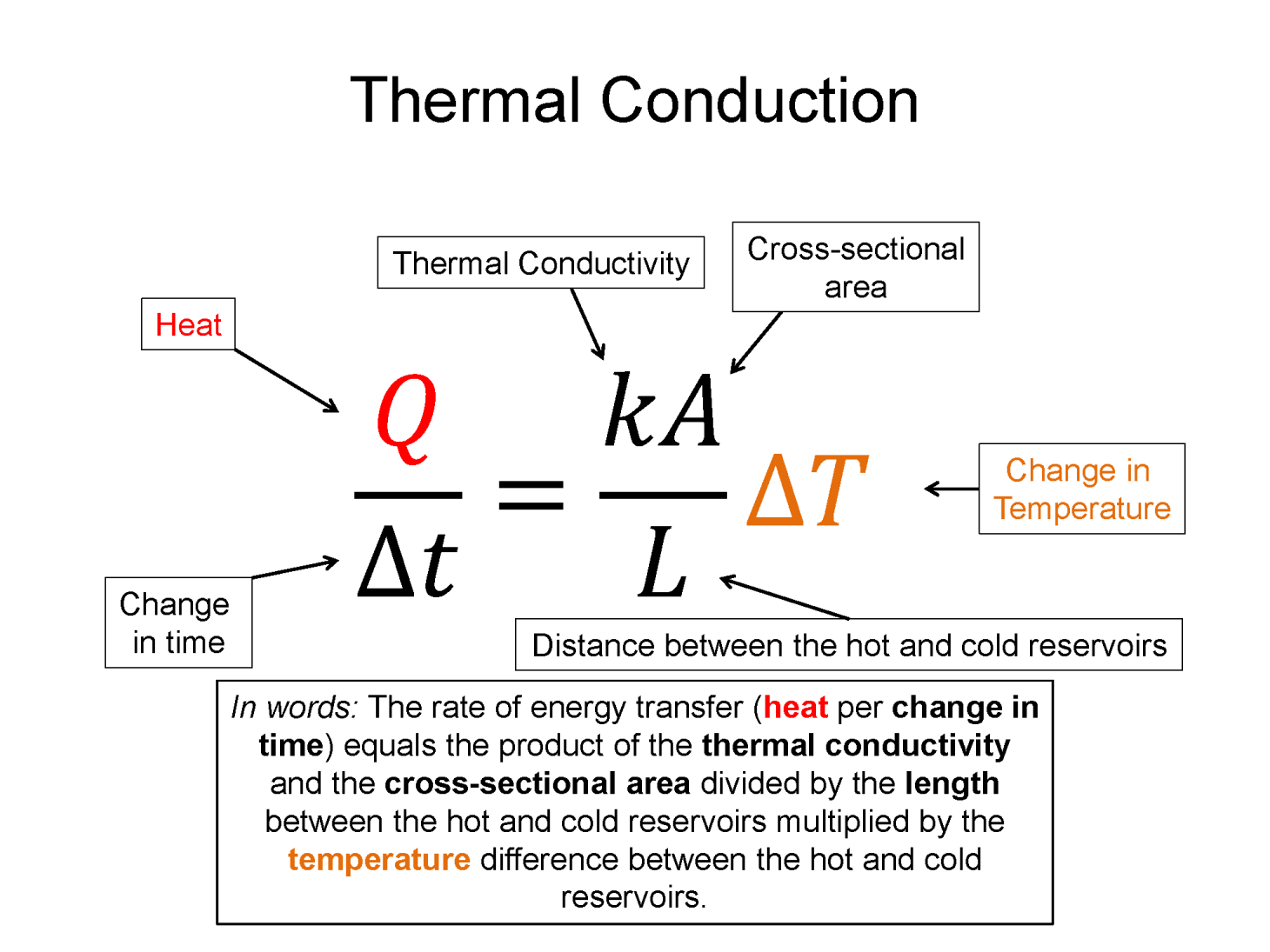
Conduction: Thermal energy, which quantifies the motion of microscopic particles, can be transferred by faster moving particles colliding with slower moving particles and transferring some of their momentum - and thus kinetic energy. Conduction is the primary heat transfer mechanism for solids, where atoms in the crystalline lattice that are wiggling a great deal due to their high thermal energy, start to make the atoms next to them wiggle more. This wiggle-transfer, from one atom to the next, is the primary conceptual understanding of conduction.
OpenStax Section 14.4 | Heat Transfer Methods
OpenStax Section 14.5 | Conduction
OpenStax Section 14.6 | Convection
OpenStax Section 14.7 | Radiation